Food Chain Definition Class 10

Have students brainstorm different biotic factorsorganisms plants and animals found in either a freshwater or marine ecosystem.
Food chain definition class 10. Grazing food chain It starts with autotrophs and goes to consumers. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other. Food chain is a sequence of organisms in a biotic community through which food passes with members of a step becoming food of the members of the next step of the sequence.
The difference between an energy pyramid and a food chain is. In scientific terms a food chain is a chronological pathway or an order that shows the flow of energy from one organism to the other. A food chain explains which organism eats another organism in the environment.
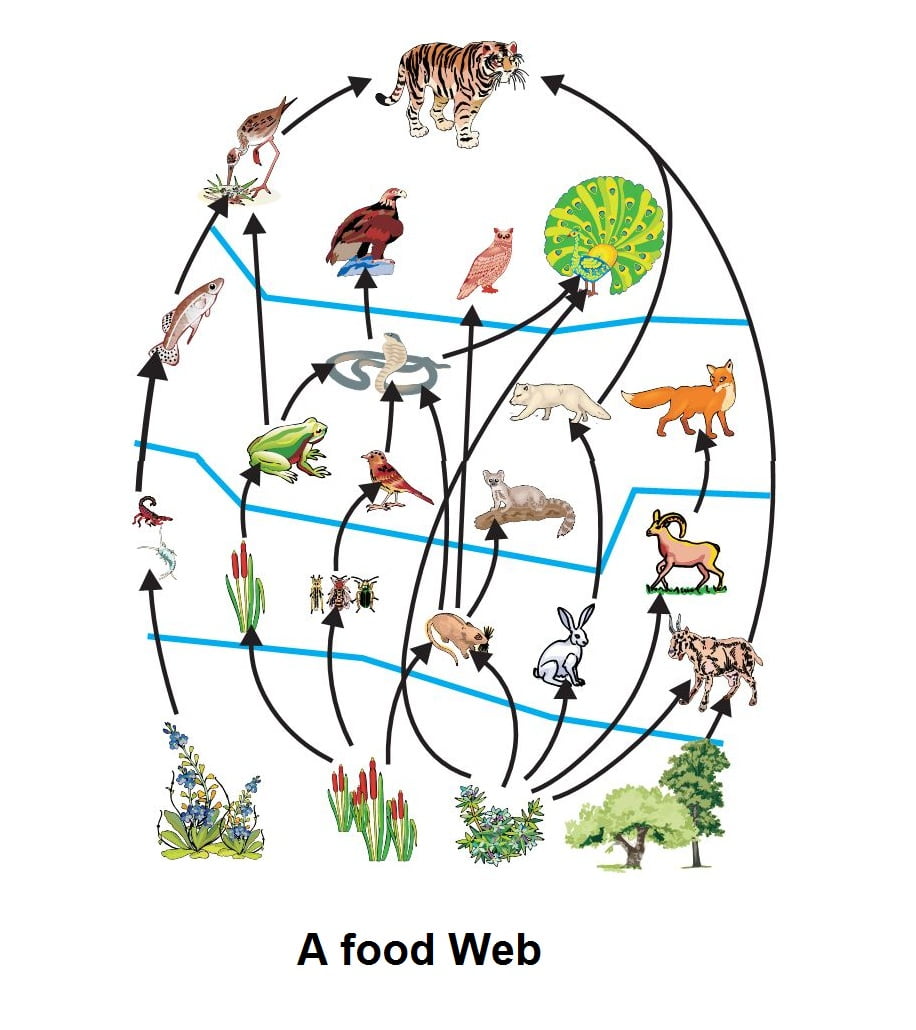
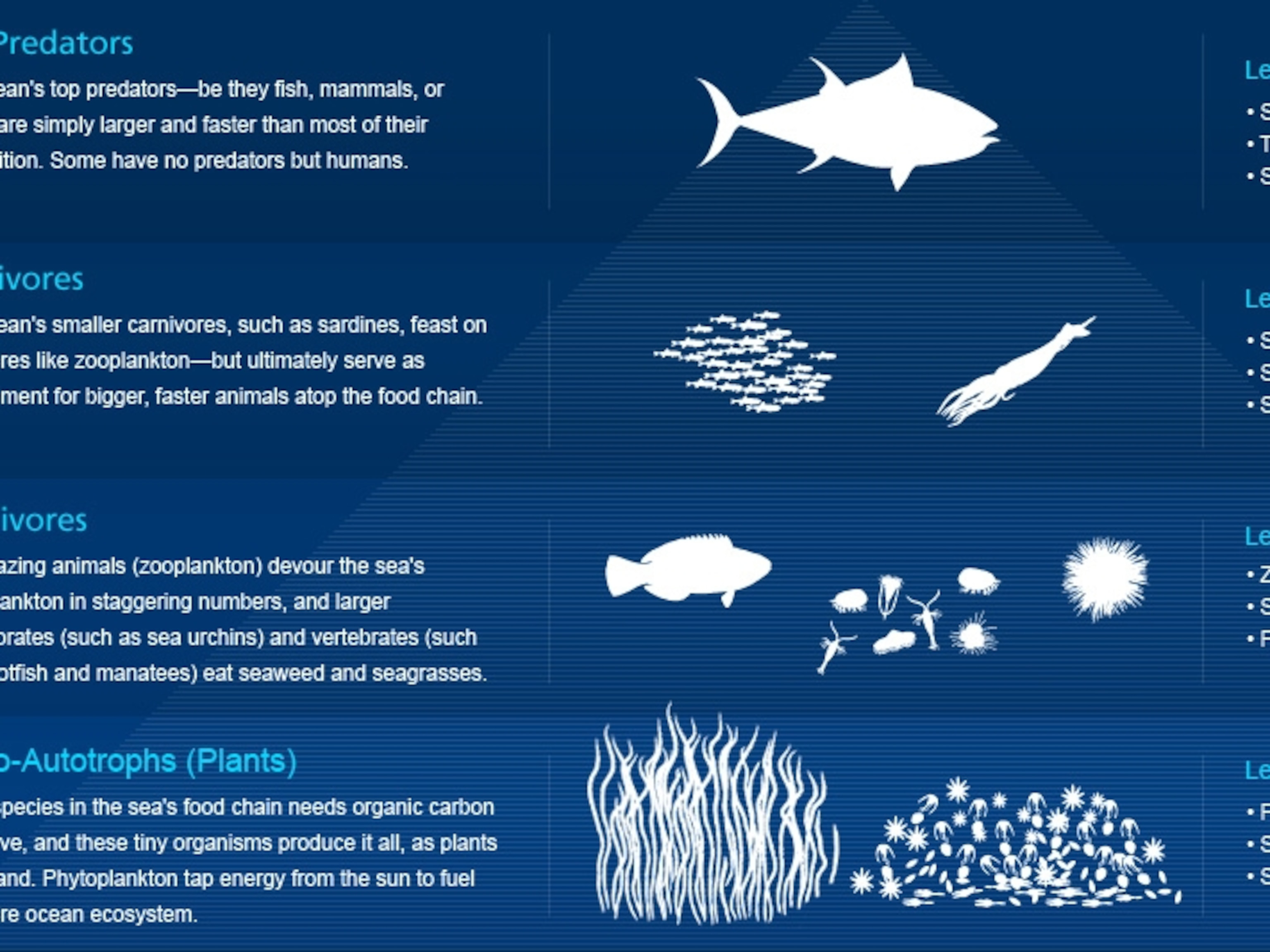
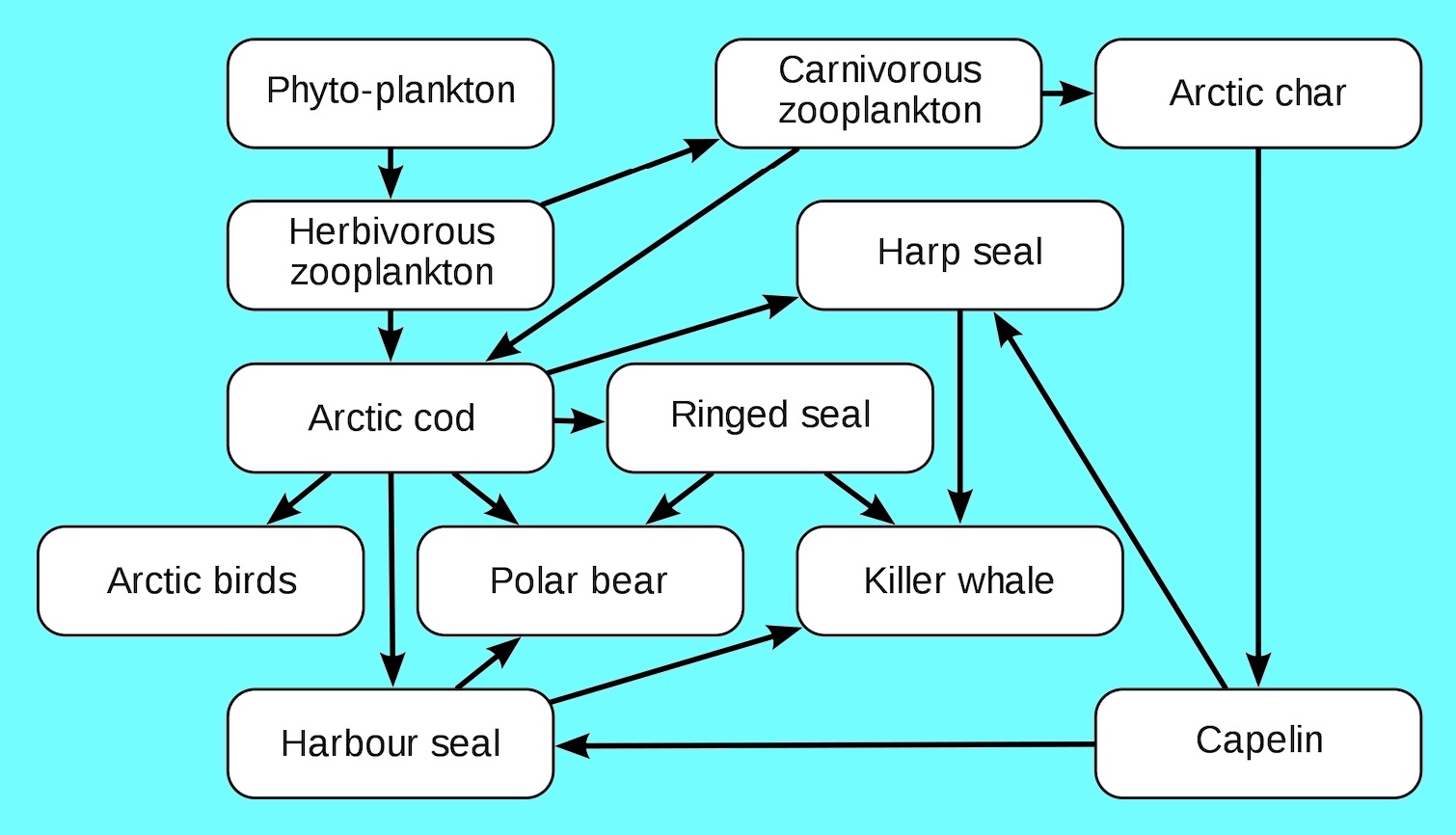
Food chains are more or less familiar to everyone in a vague sort of way. Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. 20-30 of net production is grazed on by herbivores.
The definition of food web is a model of food chains that intersect and show what eats what. Each step in the food chain is a trophic levelLets took at this food chainSo in this food chainAt the bottom level we have theproducersThey generate food to be eatenExample - PlantsThe organisms that eat the producers are calledPrimary ConsumersThey are Herbivores plant. Class 10 Biology Our EnvironmentFood chains.
Definition of Food Chain. This maintains a check on the population and a balance in the ecosystem. If occupies an intermediate trophic position between primary and secondary consumers.
What are Food chains and Explain their Characteristics. Usually there are 3 or 4 trophic levels in the food chain. Although a food chain usually shows a line of animals that eat each other it is really a never-ending cycle that.