Desert Animals Adaptations To Conserve Water

To do this they squeeze out every drop available to them and recycle it.
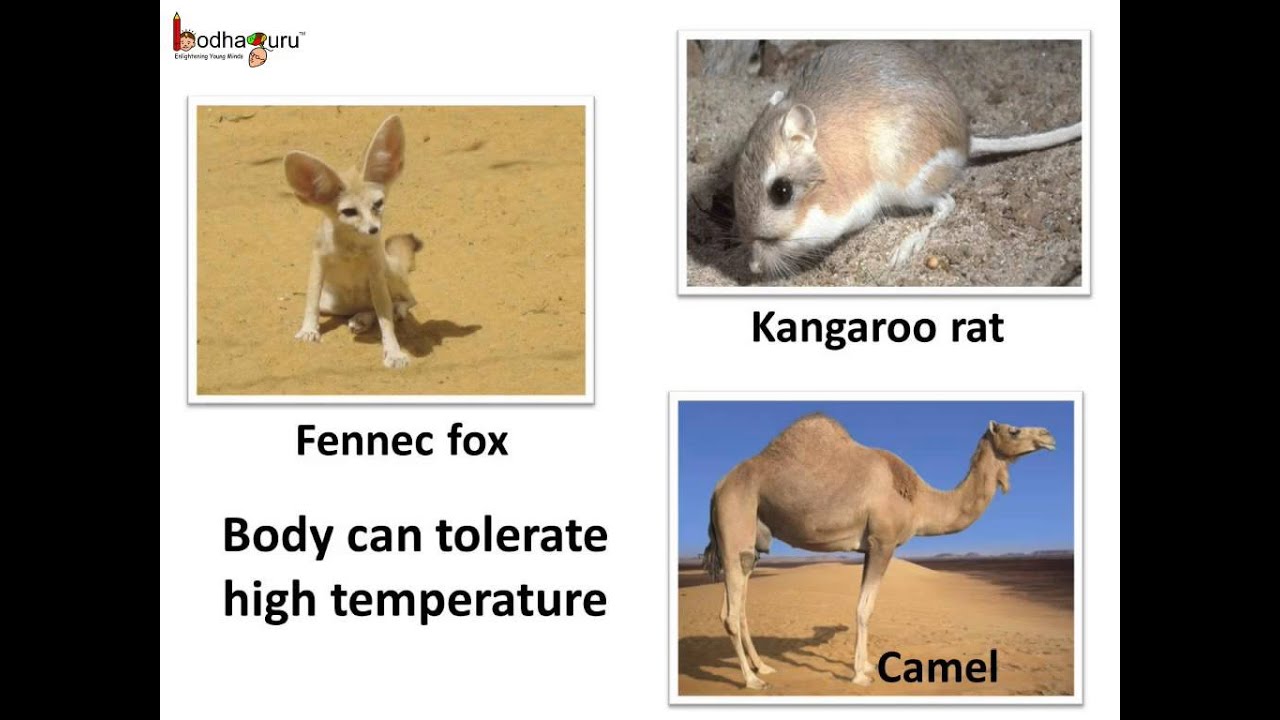
Desert animals adaptations to conserve water. The kangaroo rat which lives in the desert of southeastern Arizona is so good at conserving water that it doesnt have to drink at all. Camels arent the only animals that. Animals such as the black-tailed jackrabbit Lepus californicus are also adapted to life in the desert.
Another example of desert animals that show some classic adaptations are the kangaroo rat seen in the North American. Insects other invertebrates rodents toads desert tortoises and kit foxes use underground burrows to shelter from surface temperatures that can reach. All desert animals have learned ways and have adapted themselves either voluntarily or involuntarily to avoid the heat of the desert by simply staying out of it as much as possible.
Plant and animal bodies are made up of a number of complex biological processes which take place within a. Succulent plants seeds or the blood and body tissues of their prey. This is made possible due to the physiology of the kidney.
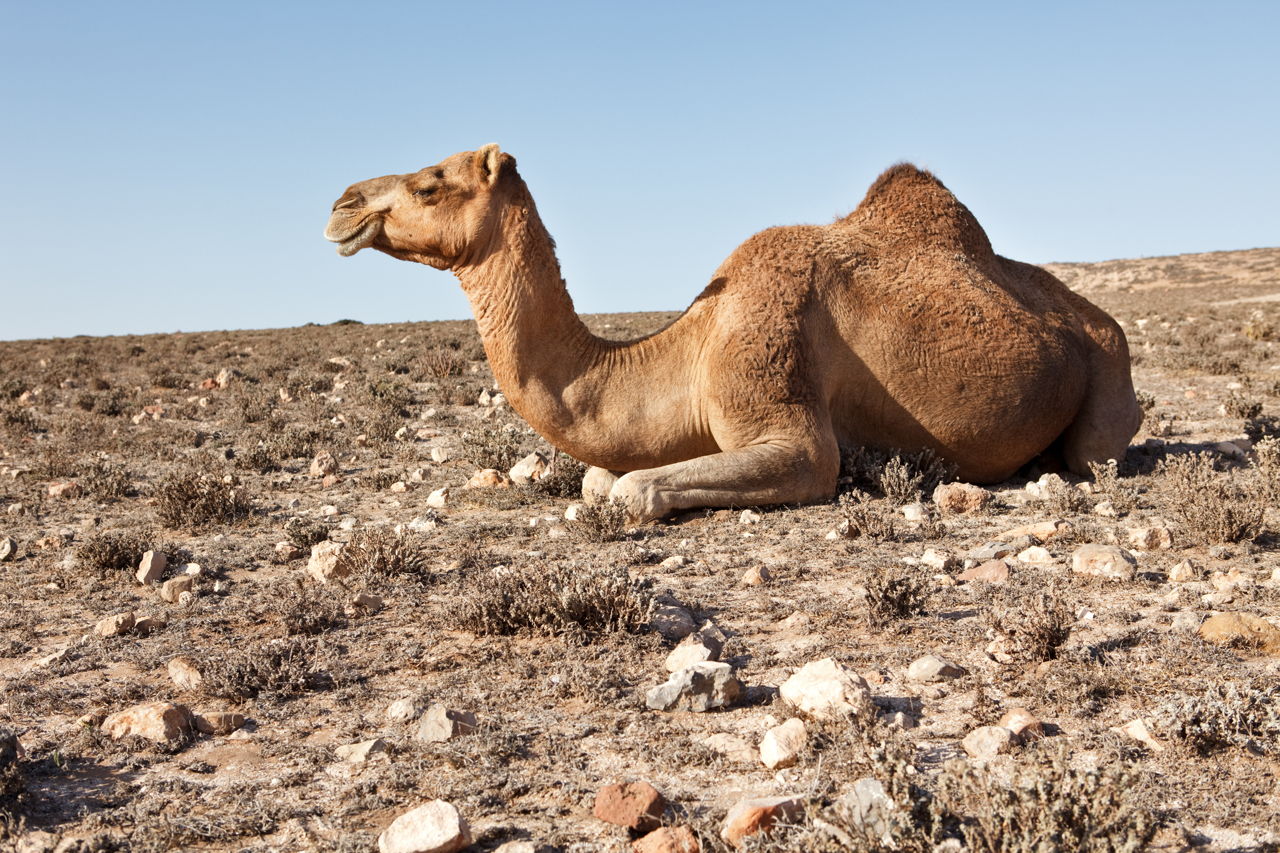
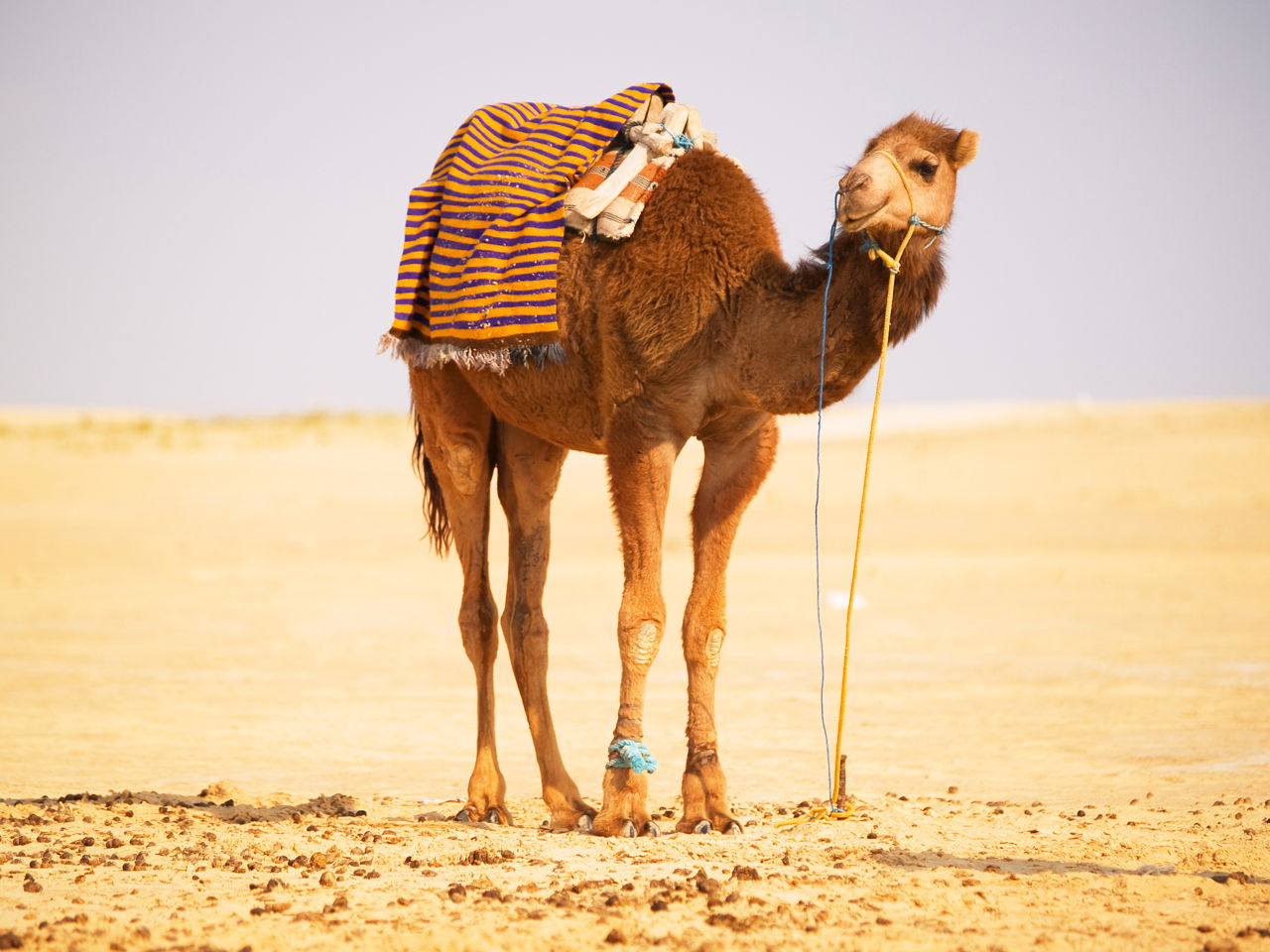
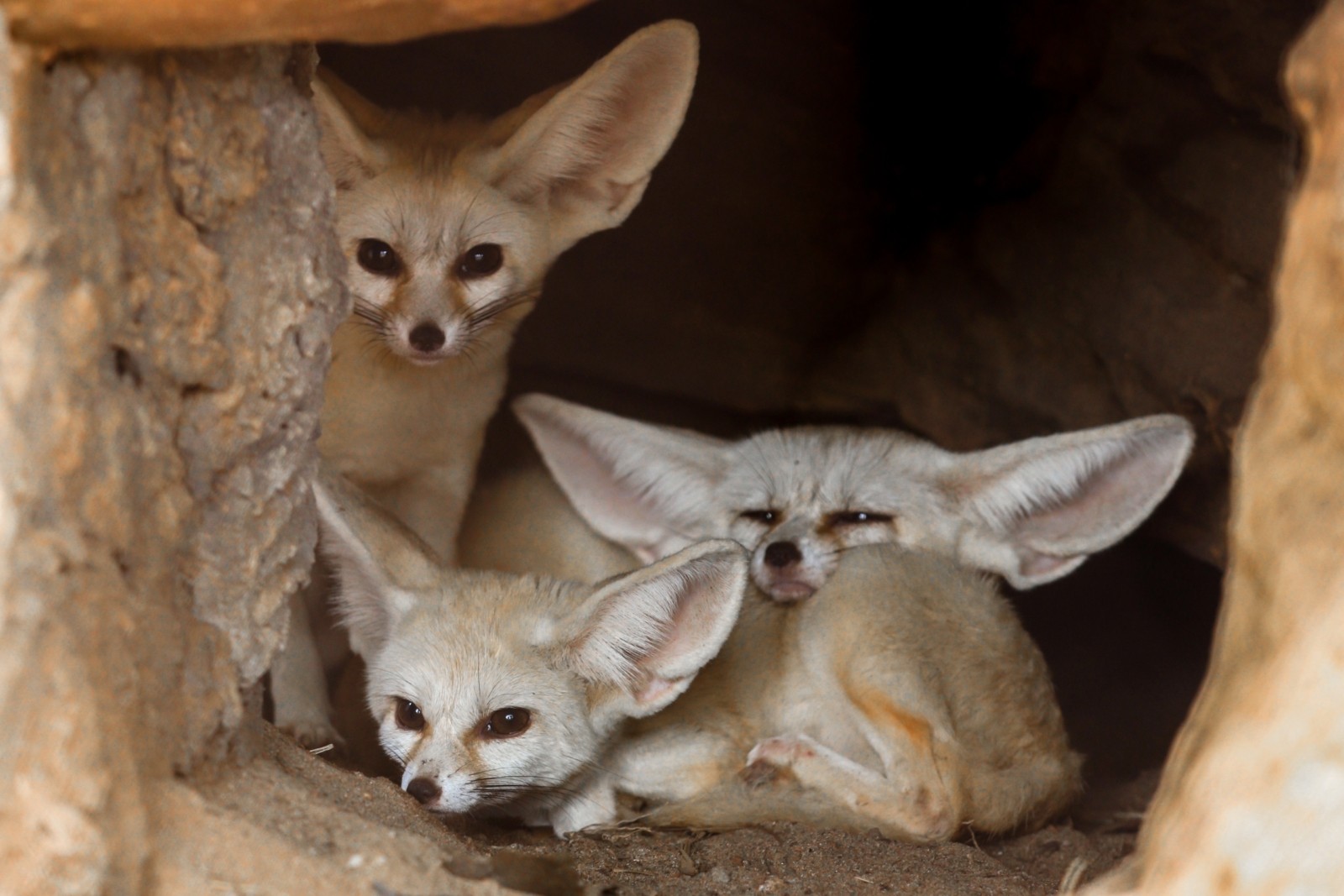
Thus adaptations of desert animals are actually the adjustments to protect themselves against high temperatures to live without water and to conserve water as far as possible. Other common adaptations seen in desert animals include big ears light-colored coats humps to store fat and adaptations that help conserve water. The main challenges xerocoles must overcome are lack of water and excessive heat.
How have animals adapted to the desert. One of the biggest water retention adaptations desert animals have is simply to avoid the sun and extreme heat. Nocturnal animals avoid activity during the.
Other common adaptations seen in desert animals include big ears light-colored coats humps to store fat and adaptations that help conserve water. A food chain is a way of showing how living organisms get their energy from each other. Cold deserts are also populated by many small mammals that horde food and are stingy about what they eat.