Cellular Respiration In Plants Equation

This process yields a lot of ATP for the plant to use for growth and reproduction.
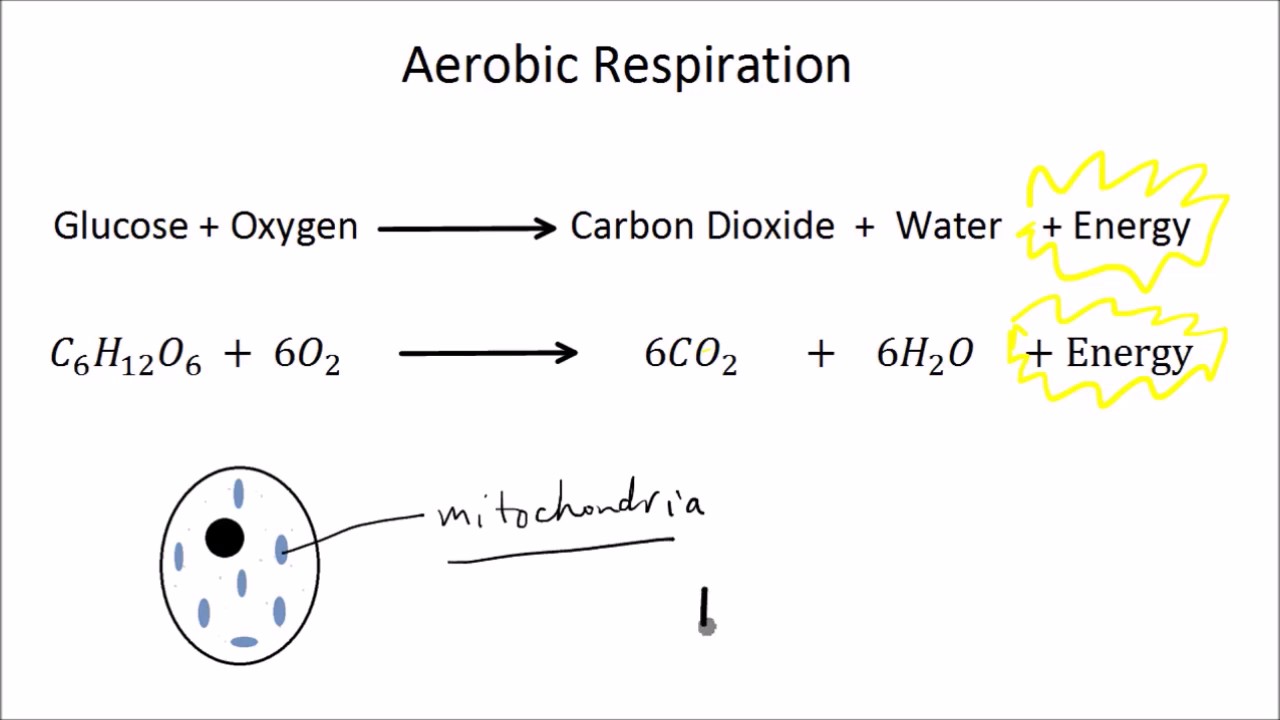
Cellular respiration in plants equation. Glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 Oxygen O 2. C 6 H 12 O 6 glucose 6O 2 36 ADP depleted ATP 36 P i phosphate groups 6CO 2 6H 2 O 36 ATP. As this stage is aerobic it does need oxygen.
Remember that respiration is not the same as breathing so take care - plants do not breathe. This process occurs in the mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell. It involves the splitting of pyruvic acid produced by glycolysis into carbon dioxide and water along with the production of adenosine triphosphate ATP molecules.
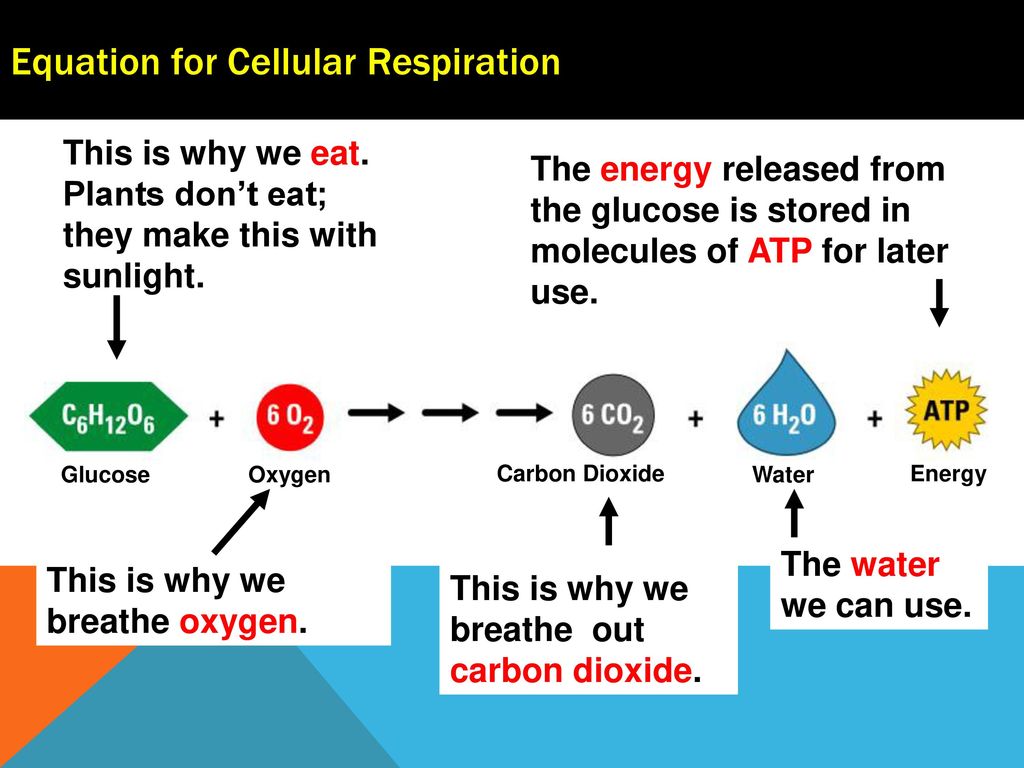
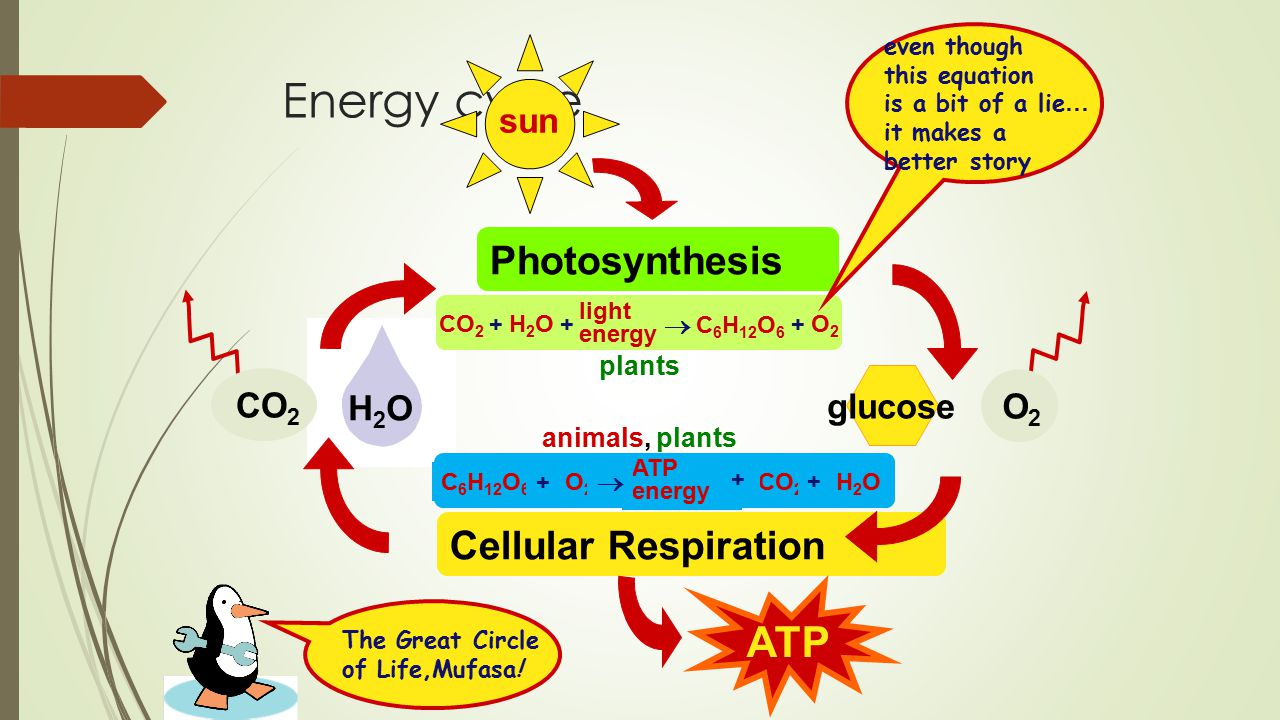
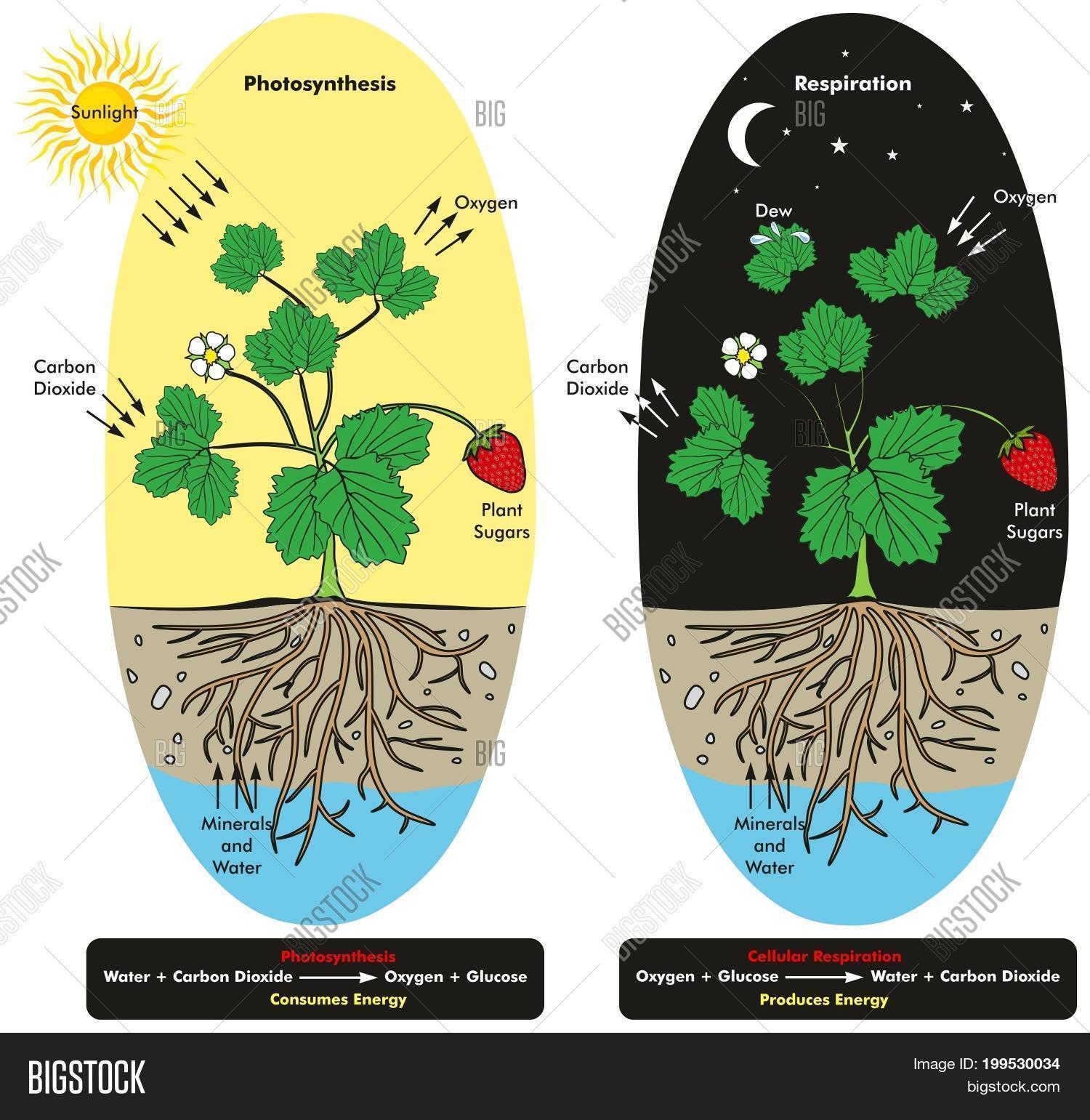
Cellular respiration is a set of biochemical reactions that takes place in most cells. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is C6H1206 6O2 6CO2 6H2O energy ATP. In hard and woody stems respiration or the exchange of gases takes place through lenticels.
In order to balance the equation for cellular respiration a 6 must be added in front of the oxygen carbon dioxide and water. Special cells in the leaves of plants called guard cells open and close the stomata. The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and ADP to produce carbon dioxide water and ATP.
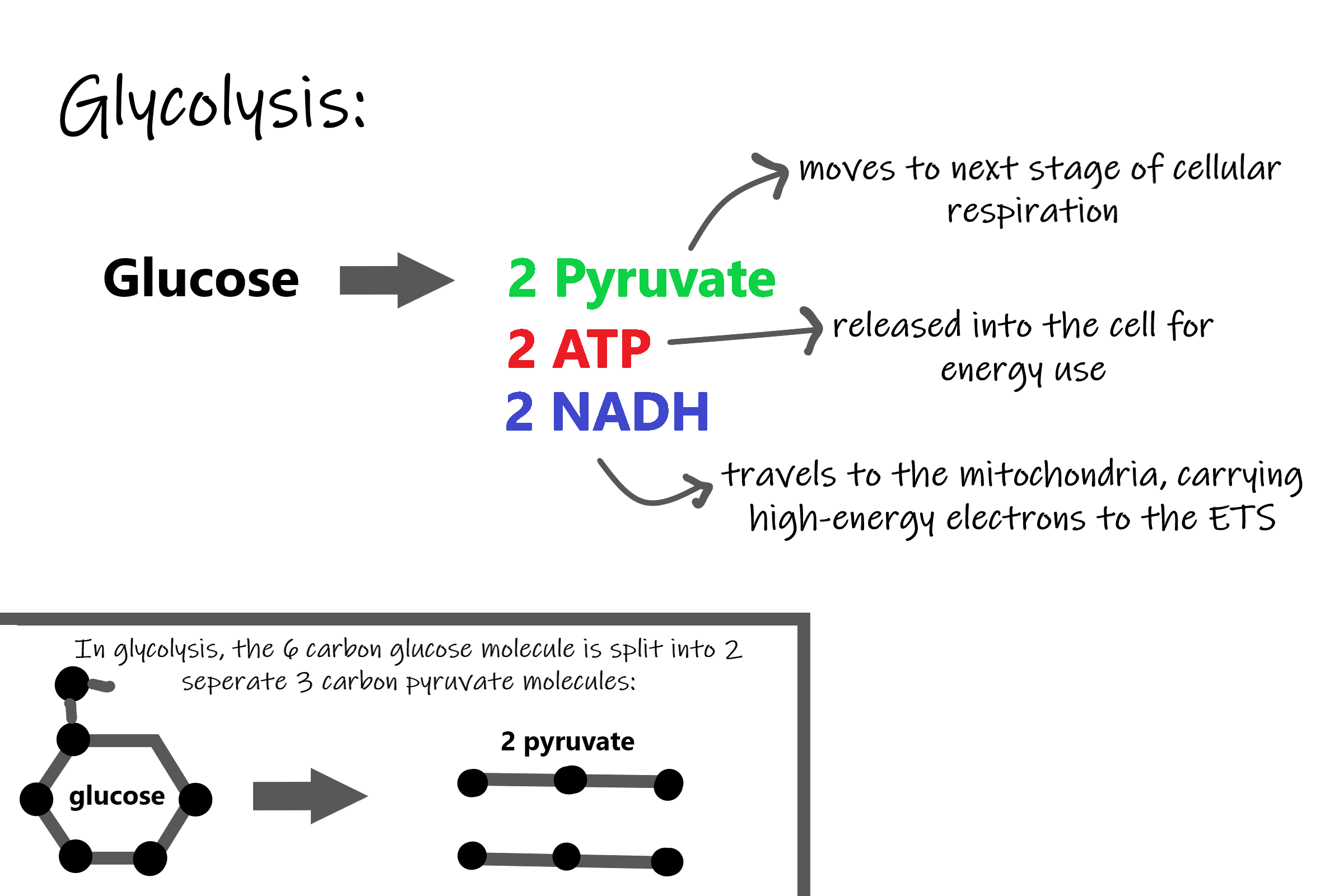
The detailed steps of cellular respiration in plants are given below. Cellular Respiration In Plants Equation. Here is the word equation for aerobic respiration.
It is also known as a catabolic reaction as a large molecule like a carbohydrate is broken down into smaller molecules. Glucose is oxidize and turned into carbon dioxide and water. C 6 H 12 O 6 1 glucose molecule 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 36 ATP ENERGY carbohydrate oxygen carbon dioxide water ATP energy 2 Description of the molecules created in all three stages of cellular respiration.