Animals In The Desert Food Chain

Of course the animals herbivores carnivores or omnivores depend totally on the plants the foundation of the food chain for survival.
Animals in the desert food chain. These animals are eaten as well by birds and foxes. Give an example of a plant and an animal that each one might eat. Detritivores and decomposers are the final part of food chains.
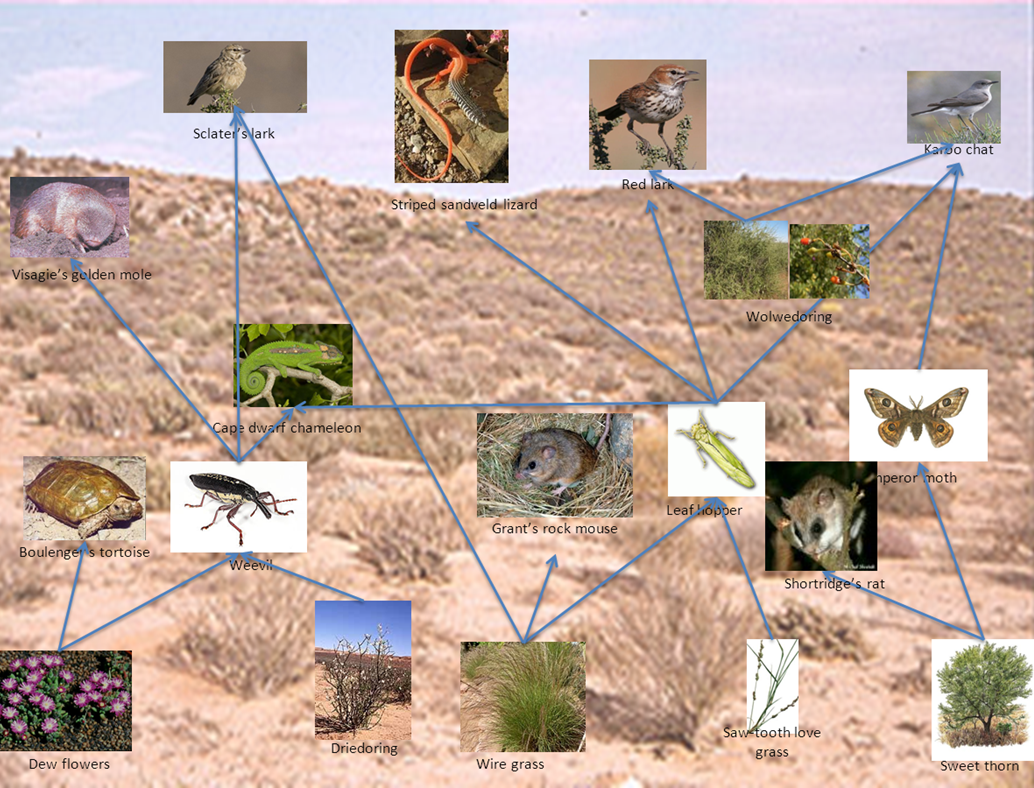
Food Chains The following food web shows the relationships between the consumers and producers specific to the Gobi desert. Food Chains and Food Webs - Balance within Natural Systems. Again we see cold-blooded animals such as snakes insect-eating lizards and tarantualas.
It can live up to 2000 years and can grow to about 24 feet wide. Detritivores are organisms that eat nonliving plant and animal remains. The hawk is like many other large predators in the desert such as a kit foxes falcons and vultures.
In the harsher desert environments they are the top predators. So a desert food chain starts with a saguaro cacti followed by a wood rat then a diamondback rattlesnake and finally a red-tailed hawk. Or another example would start with brittlebush.
These animals are fewer in numbers than the herbivores as one secondary consumer consumes many herbivores for survival. A Thorny Feast Part 4 Desert Food chain - The Yuccas Part 5 Desert Food chain - The Agave Part 6 Desert Food chain - Desert Grasslands Part 7 Desert Food chain - Desert Shrubs Part 8 Desert Food chain - The annual forbs Part 9 Desert Food chain - Mavericks of the Desert Plant. Explain the principles of the food chain and how it works in the desert.
As you can see there are many species of animals in the desert that eat each other. There is less variety within the community of organisms relative to tropical biomes or even the temperate rainforest biome of BC in the biosphere as the conditions are much harsher. Simultaneously the plants depend totally on the unpredictable desert environment.